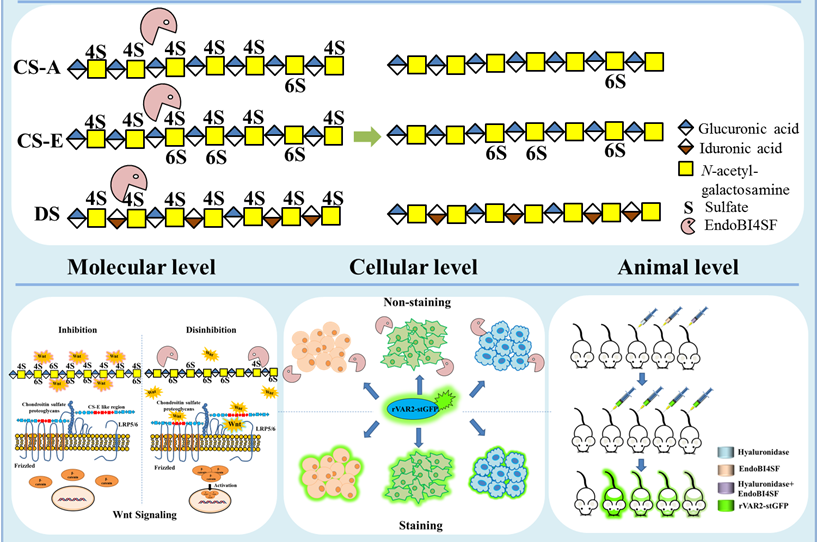
The sulfation patterns of chondroitin sulfate (CS)/dermatan sulfate (DS), which encode unique biological information, play critical roles in the various biological functions of CS/DS chains. CS/DS sulfatases, which can specifically hydrolyze sulfate groups, could potentially be essential tools for deciphering and changing the biological information encoded by these sulfation patterns. However, endosulfatase with high activity to efficiently hydrolyze the sulfate groups inside CS/DS polysaccharides have rarely been identified, which hinders the practical applications of CS/DS sulfatases. Herein, a novel CS/DS 4-O-endosulfatase (endoBI4SF) with a strong ability to completely remove 4- O-sulfated groups inside various CS/DS polysaccharides was identified and successfully used to investigate the biological roles of 4-O-sulfated CS/DS in vitro and in vivo 1 . The endoBI4SF is a much-needed tool to tailor the sulfation patterns and explore the related functions of 4-O-sulfated CS/DS chains in vitro and in vivo, and commercial available now.
Reference: Wei L, Xu Y, Du M, Fan Y, Zou R, Xu X, Zhang Q, Zhang YZ, Wang W, and Li F. A novel 4-O- endosulfatase with high potential for the structure-function studies of chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 305:120508.
For more information, visit PubMed article.
Patent number: ZL 2022 1 1300094.5
Grant date: February 13, 2024. The legal expiration date of the patent is February 12, 2044.



